Understanding the Basics of SMTP Servers
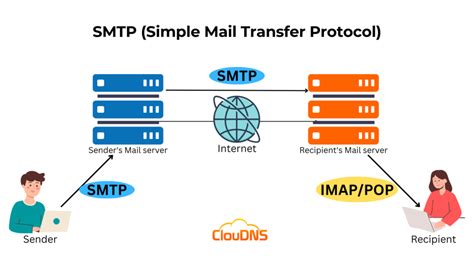
An SMTP server (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol server) is a critical component of email communication. It acts as the backbone for sending and receiving emails across the internet. Whether you're a developer, a business owner, or a regular user, understanding how an SMTP server functions is essential for effective email management.

What Does an SMTP Server Do?
The primary role of an SMTP server is to manage the sending of emails. When you send an email from your client (like Outlook or Gmail), it communicates with an SMTP server to deliver the message to the recipient's inbox. Here’s what happens behind the scenes:
- Message submission: Your email client sends the message to the SMTP server.
- Message transfer: The server relays the message to the recipient's SMTP server.
- Message delivery: The recipient's server accepts the email and places it in the inbox.
How SMTP Servers Operate
SMTP servers operate using a standardized protocol that governs the transmission of emails. Here’s a breakdown of the key operations:

- Port 25: Traditionally used for standard email transmission.
- Port 587: Used for message submission by authenticated users.
- Port 465: Used for secure SMTP (SMTPS) communication.
When an email is sent, the SMTP server uses these ports to ensure secure and reliable delivery. For instance, if you're sending an email via Gmail, your client will co
ect to Gmail’s SMTP server using Port 587 or 465, depending on whether encryption is enabled.
Types of SMTP Servers
There are different types of SMTP servers, each serving specific purposes. Understanding these types helps in choosing the right server for your needs:
- Public SMTP Servers: These are operated by email service providers like Gmail, Yahoo, or Outlook. Users can access these servers via their email client settings.
- Private SMTP Servers: Used by organizations for internal email communication. These servers are often configured on-premise and are secured with firewalls and authentication protocols.
- Third-party SMTP Servers: Companies like SendGrid, Mailgun, or Amazon SES provide hosted SMTP services for businesses. These are ideal for sending bulk emails, transactional emails, or marketing campaigns.
Setting Up an SMTP Server
Setting up an SMTP server can vary depending on the type and provider. Here’s a general overview for public and private servers:
- Public Server Setup:
- Log in to your email account (e.g., Gmail).
- Navigate to the settings and locate the SMTP server information (host, port, authentication).
- Configure your email client or application with the provided details.
- Private Server Setup:
- Install an SMTP server software (e.g., Postfix, Exchange Server).
- Configure the server with appropriate settings (IP, domain, security protocols).
- Set up user authentication and security measures.
For third-party servers, the setup usually involves registering an account, obtaining API keys or credentials, and integrating the service with your application via APIs.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount when dealing with SMTP servers. Here are some key considerations:
- Authentication: Use SMTP authentication (SMTP AUTH) to ensure that only authorized users can send emails through the server.
- Encryption: Enable SSL/TLS encryption to protect sensitive data during transmission.
- Firewall settings: Configure firewalls to allow traffic on specific SMTP ports (25, 587, 465) while blocking unauthorized access.
- Spam filtering: Implement spam filters or integrate with spam detection services to prevent abuse of the server.
By applying these security measures, users can mitigate risks associated with email spoofing, phishing, and unauthorized access.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Despite their reliability, SMTP servers can encounter issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Co
ection refused: Check the port settings and firewall configurations. Ensure the server is ru
ing and accessible. - Authentication failed: Verify user credentials and ensure SMTP AUTH is enabled.
- Message delivery failure: Review the recipient’s server status or contact their support team for assistance.
For more complex issues, contacting your SMTP provider’s support team or consulting documentation can provide additional guidance.
Advanced Features and Use Cases
SMTP servers offer advanced features tailored to specific needs. Some notable features include:
- Email tracking: Monitor when emails are opened or links are clicked.
- Delivery reports: Receive notifications on the status of sent emails (delivered, failed, deferred).
- Custom headers: Add custom metadata to emails for better tracking or analytics.
These features are particularly useful for businesses that rely on email for customer communication, marketing, or transactional notifications.
Choosing the Right SMTP Server for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate SMTP server depends on your specific requirements. Consider the following factors:
- Volume of emails: For high-volume email sending, third-party providers may offer scalable solutions.
- Security requirements: Organizations with strict security policies may prefer private servers.
- Budget constraints: Public servers are cost-effective for individual users, while enterprise-grade solutions may require paid subscriptions.
By aligning your choice with your specific needs, you can optimize your email communication and reduce potential issues.
The Role of SMTP Servers in Email Marketing
SMTP servers play a pivotal role in email marketing campaigns. Here’s how:
- Transactional emails: Send personalized messages to customers (order confirmations, password resets).
- Marketing campaigns: Deliver promotional content to a wide audience efficiently.
- Analytics: Use data from email delivery reports to improve campaign effectiveness.
Businesses leveraging SMTP servers for marketing can enhance their outreach and improve customer engagement.
SMTP Server Configuration Best Practices
To ensure optimal performance and security, follow these best practices for SMTP server configuration:
- Use secure authentication: Always enable SMTP AUTH and use strong passwords or API keys.
- Enable encryption: Use SSL/TLS to encrypt data in transit.
- Monitor logs: Regularly review server logs for anomalies or suspicious activity.
- Update regularly: Keep server software updated to address vulnerabilities and improve performance.
Adhering to these best practices helps maintain a secure and efficient email communication system.
Integration with Email Clients and Applications
Integrating SMTP servers with email clients and applications is crucial for seamless email sending. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Email clients: Use the SMTP server settings provided by your email service (e.g., host, port, authentication).
- Applications: For developers, integrate SMTP via APIs or libraries (e.g., Node.js, Python SMTP libraries).
For developers, creating a custom integration using APIs ensures flexibility and scalability in email sending capabilities.
Conclusion
In summary, an SMTP server is a cornerstone of modern email communication. Whether you’re managing personal emails, ru
ing a business, or executing marketing campaigns, understanding how SMTP servers operate and choosing the right server for your needs is essential. By following best practices for setup, security, and configuration, users can maximize the efficiency and reliability of their email systems.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of SMTP servers will remain vital. Stay informed and adapt your strategies to leverage the power of email communication effectively.