Understanding the Basics of SMTP Service
SMTP, or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is a cornerstone of modern email communication. Whether you're sending a personal email or managing a corporate email server, SMTP is the engine that ensures your messages reach their destination. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into what SMTP service is, how it works, and why it’s essential for anyone involved in digital communication.
What Exactly Is SMTP?
SMTP is a standardized protocol used for sending, receiving, and relaying email messages over the internet. Developed in the early days of email (the 1980s), SMTP has evolved significantly to accommodate the needs of a rapidly growing digital world. Essentially, it acts as the postal service for email, directing messages from the sender to the recipient through a network of servers.
How SMTP Works: A Step-by-Step Explanation
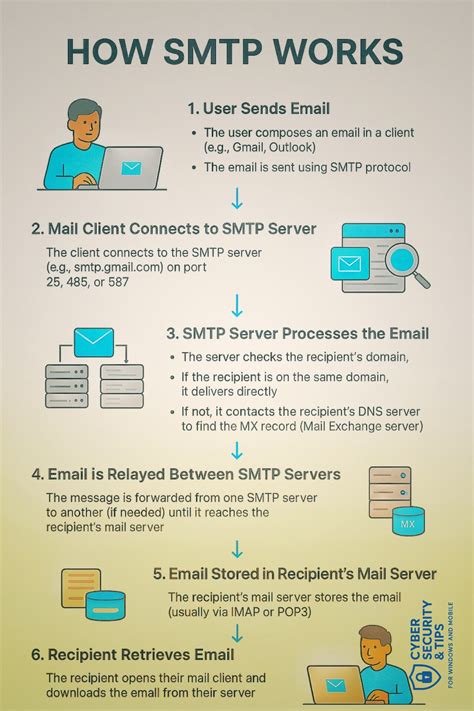
To understand how SMTP operates, let’s break down the process into a few key steps:
- Message Composition: The user composes an email using an email client (like Outlook or Gmail).
- Authentication: The client authenticates the sender’s credentials (username and password) before sending the message.
- Message Transfer: The email is sent to the SMTP server via a port (typically port 25 for standard transmission, port 587 for secure transmission).
- Routing: The SMTP server determines the recipient’s server and routes the message accordingly.
- Delivery: The recipient’s server receives the message and delivers it to the user’s inbox.
This process may seem simple, but it involves complex interactions between servers to ensure accuracy, reliability, and security.
Key Components of SMTP Service
Understanding the components of SMTP service helps users better appreciate how their messages are managed. Here are the main elements:
- Mail Transfer Agent (MTA): The MTA is responsible for transferring messages between servers. Tools like Sendmail, Postfix, and Microsoft Exchange are common MTAs.
- Mail Delivery Agent (MDA):strong> The MDA handles the delivery of messages to the recipient’s mailbox. This can be integrated into the MTA or run as a separate service.
- Mail User Agent (MUA):strong> The MUA is the user-facing application—like Outlook or Thunderbird—that allows users to compose and send emails.
Together, these components form a cohesive system that supports seamless email communication.
Types of SMTP Services
SMTP services vary based on their use cases and functionalities. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
- Public SMTP Services: These are offered by email providers like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook. They are user-friendly and ideal for personal or small business use.
- Private SMTP Services: Often used by corporations and enterprises, private SMTP services are customized to meet specific organizational needs. These services may include features like encryption, advanced authentication, and internal routing.
- Cloud-Based SMTP Services: With the rise of cloud computing, cloud-based SMTP solutions like Amazon SES, SendGrid, and Mailgun have become popular. These services offer scalability, reliability, and cost-effective solutions for businesses of all sizes.
Choosing the right SMTP service depends on your specific requirements, whether it’s scalability, security, or ease of use.
Why SMTP Service Matters for Businesses
For businesses, SMTP service is more than just a technical tool—it’s a critical infrastructure component. Here’s why:
- Reliability: SMTP ensures that emails reach their destination without u
ecessary delays or loss. - Security: With features like TLS encryption and SPF/DKIM/DMARC, SMTP helps protect emails from spam and phishing attacks.
- Scalability: Cloud-based SMTP services allow businesses to scale their email operations as their user base grows.
- Compliance: Many industries require email communication to comply with specific regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). SMTP services help ensure compliance by providing audit trails and logs.
Without a reliable SMTP service, businesses risk losing communication with clients, customers, and partners.
SMTP vs. Other Email Protocols
To fully appreciate SMTP’s role, it’s important to compare it with other email-related protocols:
- SMTP (Sending): Used for sending messages from the sender to the recipient’s server.
- POP3 (Receiving): Used by clients to download messages from the server to their local device.
- IMAP (Receiving): Used by clients to access messages stored on the server without downloading them.
While SMTP is focused on sending, POP3 and IMAP are used for retrieving emails. Understanding these distinctions helps users configure their email clients correctly.
Setting Up SMTP Service: A Practical Guide
Setting up an SMTP service can vary depending on the provider and the user’s technical expertise. Here’s a general step-by-step guide:
- Choose an SMTP Provider: Select a provider based on your needs (public, private, or cloud-based).
- Register or Log In: Create an account or log in to your existing one.
- Configure Server Settings: Enter the SMTP server address, port number, and authentication details (username/password).
- Test the Co
ection: Send a test email to ensure the setup is working correctly.
For users who are less technically inclined, many providers offer detailed guides or support to assist with the configuration process.
Common SMTP Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Despite its reliability, users may encounter issues with SMTP service. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Authentication Errors: If you’re receiving an error related to login credentials, double-check your username and password. Ensure you’re using the correct authentication method (e.g., OAuth2, SMTP Auth).
- Port Blocking: Some ISPs block standard SMTP ports (e.g., port 25). If you’re unable to send emails, try switching to a different port (e.g., port 587 or port 465).
- Message Rejection:** If your messages are being rejected, check the content for spam triggers—like suspicious links or attachments—and ensure your SPF/DKIM/DMARC settings are configured correctly.
- Co
ection Issues:** If the co
ection to the SMTP server is failing, verify the server address and port number. Use online tools like MX lookup to confirm server details.Having a solid understanding of these issues and their solutions can save time and reduce frustration.
 Asset Ref: SMTPmeaning
Asset Ref: SMTPmeaningThe Role of SMTP in Email Security
Email security is a growing concern, and SMTP plays a vital role in mitigating risks. Here’s how:
- TLS Encryption: Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts messages during transmission, ensuring that sensitive information isn’t exposed to third parties.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): SPF verifies that the email sender’s domain is authorized to send messages on behalf of the domain.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): DKIM adds a digital signature to emails to confirm authenticity.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance): DMARC combines SPF and DKIM to provide a framework for handling emails that fail authentication.
Together, these security protocols form a robust defense against spam, phishing, and other malicious activities.
Benefits of Cloud-Based SMTP Services
Cloud-based SMTP services have revolutionized the way businesses manage their email infrastructure. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Scalability: Cloud services allow businesses to handle large volumes of emails without upfront infrastructure costs.
- Reliability: With redundant servers and built-in backup systems, cloud SMTP services ensure high availability and uptime.
- Cost-Effectiveness:** Cloud-based solutions eliminate the need for maintaining in-house servers, reducing operational expenses.
- Advanced Features:** Many cloud SMTP services offer additional features like analytics, spam filtering, and automated routing.
For growing businesses, cloud-based SMTP services provide a scalable, secure, and efficient solution.
Choosing the Right SMTP Service for Your Needs
Selecting the right SMTP service depends on several factors. Consider the following checklist when making your decision:
- Use Case: Determine whether you need a public, private, or cloud-based service.
- Scalability Requirements: Assess your expected email volume and choose a service that can accommodate your growth.
- Security Needs:** Evaluate the security features offered by the service—encryption, authentication protocols, etc.
- Cost:** Compare pricing models and determine which service offers the best value for your budget.
By aligning your choice with your specific requirements, you can ensure a seamless email experience.
Future Trends in SMTP Service
As technology evolves, so does SMTP service. Here are some emerging trends to watch:
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence is being used to improve spam detection, content filtering, and message routing.
- Enhanced Security Protocols:** Newer encryption standards and authentication methods are continuously being developed to enhance email security.
- Integration with Other Platforms:** SMTP services are increasingly being integrated with collaboration tools, CRM systems, and marketing platforms to streamline workflows.
These trends indicate a continued evolution of SMTP service to meet the demands of a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Conclusion: Why Understanding SMTP Service Is Essential
In conclusion, SMTP service is a fundamental component of modern communication. Whether you're an individual user or a business owner, understanding how SMTP works, its components, and its importance can significantly enhance your email experience. From ensuring reliable message delivery to safeguarding against security threats, SMTP plays a critical role in the digital world. As the landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about SMTP service will help you adapt and thrive.
Final Thoughts
Don’t underestimate the power of SMTP. It’s more than just a protocol—it’s the backbone of email communication. By leveraging the right SMTP service and understanding its capabilities, you can communicate more effectively, securely, and efficiently.

